What is a Titanium Plate Used For? Exploring Its Applications and Benefits
Titanium is a remarkable metal known for its strength, light weight, and exceptional resistance to corrosion. Among its various forms, titanium plates are especially popular across industries for their versatility and performance. These plates are used in everything from aerospace components to medical implants, making them essential in high-performance environments. In this article, we’ll explore the diverse applications of titanium plates, their key benefits, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Titanium Plate?
A titanium plate is a flat, rigid sheet made from titanium metal, which is prized for its strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. Available in different grades such as Grade 2 (commercially pure titanium) and Grade 5 (titanium alloy), each grade offers distinct properties suited to specific applications. Titanium’s lightweight and durable nature make it an ideal choice for industries requiring materials that can withstand harsh environments without compromising performance.
Key Properties of Titanium:
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium plates excel in corrosive environments, making them ideal for use in industries like aerospace, marine, and chemical processing.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium is much lighter than steel but just as strong, which makes it essential in applications where reducing weight without sacrificing strength is crucial.
Biocompatibility: In medical and dental fields, titanium is highly valued for its ability to integrate with the human body without causing adverse reactions.
Key Benefits of Titanium Plates
Titanium plates offer several key advantages that make them indispensable in various applications:
Durability: Titanium’s corrosion resistance allows it to thrive in challenging environments, such as high salt concentrations or acidic conditions. This durability ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs.
Lightweight and Strong: Titanium plates are prized for their high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes them a perfect choice for industries like aerospace and automotive, where weight savings are critical for performance.
Heat Resistance: Titanium can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, making it suitable for use in high-heat applications such as turbine engines and exhaust systems.
Biocompatibility: Due to its non-reactive nature, titanium is widely used in medical implants, such as joint replacements and dental implants, where compatibility with the human body is essential.
Common Applications of Titanium Plates
Titanium plates are used in a wide range of industries, thanks to their unique properties. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common applications:
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, titanium is essential for manufacturing aircraft parts that must endure high stress, pressure, and temperature changes. Common uses include:
Aircraft Components: Titanium is used in the construction of wings, fuselages, and engine components, where its strength and lightness improve fuel efficiency and performance.
Turbine Engines: Titanium’s ability to withstand high temperatures without losing structural integrity makes it ideal for use in turbine blades and other critical engine components.
Exhaust Systems: Titanium is also used in aircraft exhaust systems due to its resistance to extreme heat and corrosion.
Marine Industry
The harsh conditions of the marine environment make titanium plates an essential material for many applications:
Shipbuilding: Titanium’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for ship hulls and other underwater structures that are exposed to saltwater.
Submarines: The metal's strength and resistance to pressure make it a preferred choice in the construction of submarines and deep-sea equipment.
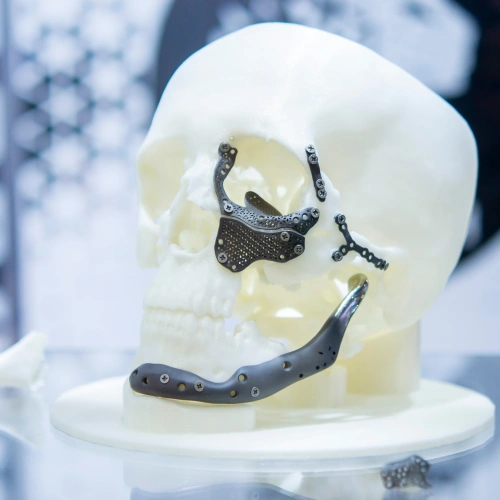
Medical and Dental Applications
Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it a top choice in the medical field:
Implants: Titanium plates are used in joint replacements, dental implants, and spinal surgeries due to their ability to integrate seamlessly with human tissue.
Surgical Instruments: Titanium’s non-reactive properties reduce the risk of infection, making it ideal for surgical tools and medical devices.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector also benefits from titanium’s properties, particularly in high-performance vehicles:
Exhaust Systems: Titanium is used in exhaust systems of sports and racing cars for its heat resistance and lightweight nature.
Engine Components: Performance vehicles use titanium in engine parts, reducing weight and enhancing efficiency without sacrificing strength.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industries
Titanium’s corrosion resistance makes it an invaluable material in chemical processing, especially in environments where metals are exposed to harsh chemicals or high temperatures:
Heat Exchangers: Titanium plates are used in heat exchangers for their ability to resist corrosion in acidic or corrosive environments.
Piping Systems: Titanium’s durability and resistance to chemicals make it ideal for reactors, pipes, and other components in petrochemical plants.
Use of Titanium Plates in Consumer Products
While titanium is largely used in industrial and medical applications, its unique properties also make it popular in consumer goods:
Jewelry: Titanium is increasingly used in rings, bracelets, and other jewelry items. Its hypoallergenic properties, along with its sleek and modern look, make it a popular choice for high-end fashion.
Sports Equipment: Due to its strength and lightness, titanium is used in high-performance sports equipment such as golf clubs, bicycle frames, and tennis rackets.
Watches: Titanium’s scratch resistance and lightweight nature make it a preferred material for premium watches, ensuring long-lasting durability.
Titanium Plate Manufacturing Process
The production of titanium plates involves several key stages that ensure the material meets specific industry standards. Here’s an overview of the manufacturing process:
Extraction of Raw Titanium: Titanium is extracted from minerals like rutile or ilmenite. The ore is refined into titanium sponge, which is the starting point for most titanium products.
Alloying and Melting: The titanium sponge is melted in a furnace, and alloys may be added to enhance specific properties like strength or heat resistance.
Forming and Rolling: The molten titanium is formed into thick sheets or plates by hot or cold rolling. The thickness and shape are adjusted to meet the requirements of different applications.
Heat Treatment and Finishing: The titanium plates are heat-treated to relieve stress and improve strength. Surface finishing processes like polishing or coating may also be applied to meet aesthetic or functional needs.
How to Choose the Right Titanium Plate for Your Application
Choosing the right titanium plate depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your application. Here’s what you should consider:
Grade of Titanium: Titanium comes in different grades, each offering unique properties. For example, Grade 2 is commercially pure and provides excellent corrosion resistance, while Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is stronger and more heat-resistant, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
Thickness and Size: The required thickness and dimensions of the titanium plate will depend on the specific application. Thicker plates may be needed for structural applications, while thinner plates may suffice for lighter applications.
Surface Finish: Depending on the use case, the surface finish may be important. Smooth finishes are essential for implants or aesthetic products like jewelry, while industrial applications may tolerate rougher surfaces.
Titanium plates are indispensable in many industries due to their strength, lightweight nature, and exceptional resistance to corrosion. Whether used in aerospace components, medical implants, or consumer products, titanium plates offer a unique combination of durability and versatility. Understanding their key properties and applications can help you make informed decisions when selecting titanium plates for your specific needs.
Contact us today to learn more about our Weld Neck Flange options and get a quote for your next project.
FAQs
What are the advantages of titanium plates over other metals?
Titanium plates offer superior strength without the weight of materials like steel, making them ideal for weight-sensitive applications. They also outperform many metals in terms of corrosion resistance and heat resistance.
How long do titanium plates last in high-stress environments?
Titanium plates can last for decades in high-stress environments, thanks to their durability and resistance to corrosion. This longevity is one of the key reasons titanium is used in industries like aerospace and marine.
Are titanium plates eco-friendly?
Yes, titanium is a sustainable material. It’s highly durable, meaning it doesn’t need to be replaced frequently. Additionally, titanium is 100% recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly choice.https://www.shnadonggroup.com/products/titanium-sheet-plate.html

